While melanin-rich skin naturally offers more protection from sun damage than lighter skin, that does not mean sunscreen is optional. People with darker skin tones and melanin-rich skin have inherent sun protection in the range of SPF 8-13, so they don’t burn as easily and experience skin aging that begins at older ages and in different, less apparent ways.
Nevertheless, deeper skin tones are at risk for the same cumulative destruction sun exposure causes those with lighter skin tones including increased fine lines and wrinkles. More studies have shown the danger of delayed skin cancer diagnoses for people of color, thus the importance of wearing sunscreen is clear.
Research has shown that people with darker skin color are generally more vitamin D–deficient. This is due to the higher amounts of melanin in darker skin blocking the sun’s UVB rays enough to inhibit vitamin D production.
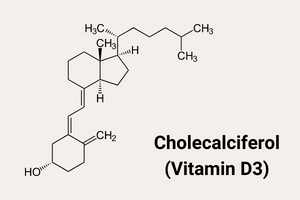

Vitamin D3 is produced by a photochemical reaction from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the epidermis. UVB irradiation of the skin converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to pre-vitamin D3, followed by a thermal reaction to produce vitamin D3.
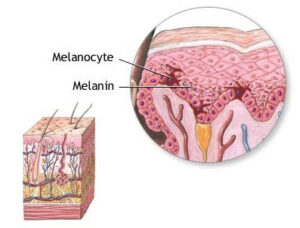
Consequently, the production is, at least, determined by the amount of radiation and is influenced by sunscreens, clothing, and skin pigmentation. Skin pigmentation is largely determined by the concentration and type of melanin in epidermal keratinocytes.
Melanin is a large opaque polymer that is produced constitutively. In response to UV radiation, melanin distribution alters, and synthesis increases in the skin. Melanin effectively absorbs and scatters electromagnetic radiation across the entire UV and visible light range and thus competes with 7-dehydrocholesterol for UVB rays.
Consequently, skin pigmentation hinders the transformation from 7-dehydrocholesterol to vitamin D3.
Even though these lower levels of vitamin D, sunscreen is crucial and cannot be avoided! We suggest the use of sunscreen with at least SPF 30, which provides broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB light, with a lightweight feel on the skin, gentle enough for sensitive skin, and with some vitamin D precursors that could in an alternative way activate and stimulate vitamin D production.

The development of cosmetic products for melanin-richer skin types requires a high level of knowledge about the composition of these particular skin types. The needs of these skin types are very different from Caucasian skin and must be taken into account during the product development in order to offer effective cosmetics for melanin-rich skin types.

Are you looking for science-based skin and hair care and environmentally friendly cosmetic products? Then we are the perfect partner for you.